Что такое частота кроссовера Fc, наклоны кроссовера и почему они важны?
Кроссоверы чрезвычайно важны для акустических систем и больших причина, по которой мы можем получить качество звука, которое нам нравится.
С другой стороны, такие вещи, как частота кроссовера (Fc), наклоны (дБ на октаву) и то, как все это работает, могут быть немного сложными, если вы не понимаете, как все это работает. Я был бы рад помочь!
В этой статье я объясню:
- Что такое частота кроссовера Fc и почему это важно
- Что такое перекрёстный уклон и наиболее распространённый из них
- Как рассчитать падение кроссовера в дБ для частот, включая Fc
- Роль катушек индуктивности и конденсаторов (и «реактивное сопротивление» для Fc)
Объяснение частоты кроссовера Fc и наклонов кроссовера
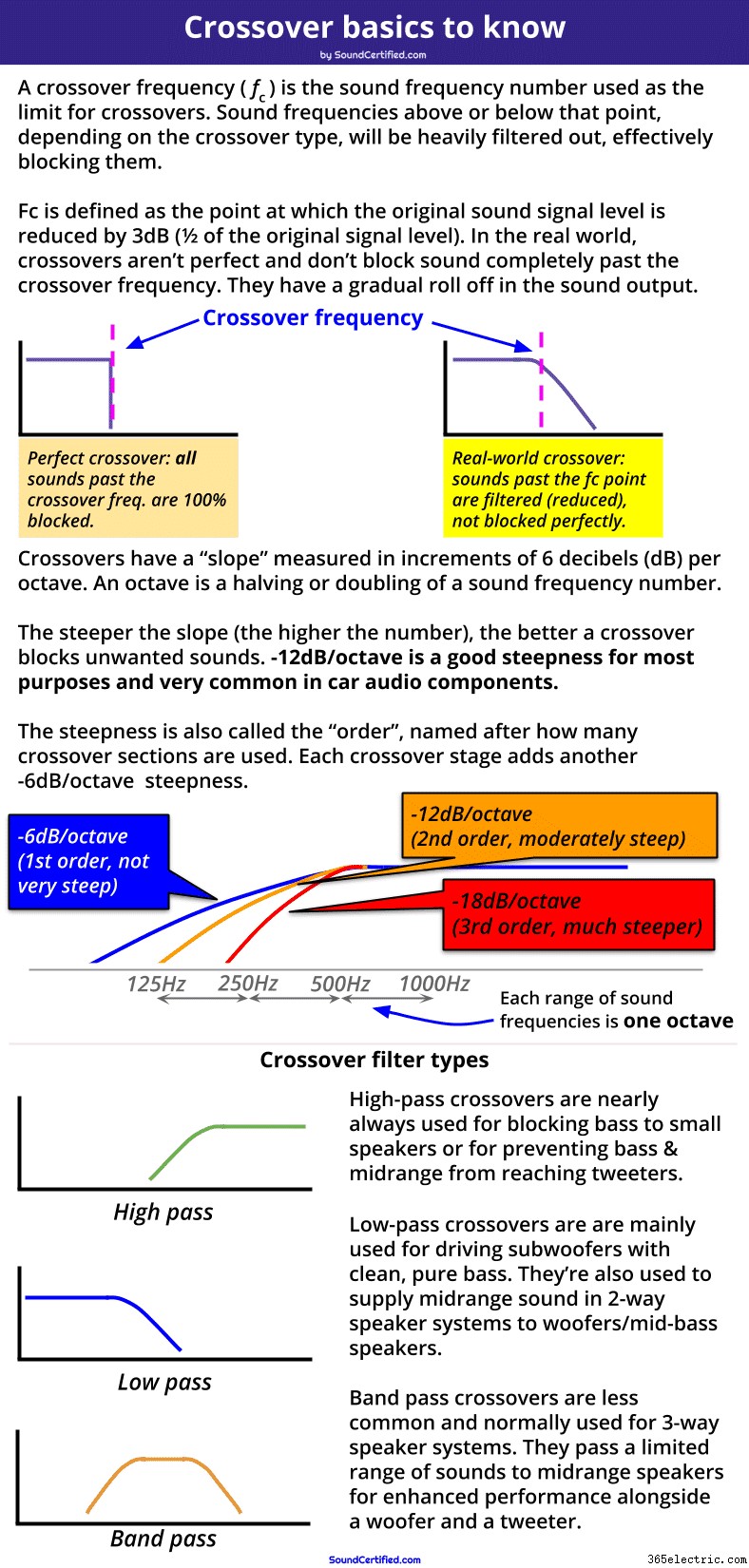
На этой диаграмме показаны примеры трех основных типов фильтров, используемых в кроссоверах. Также показаны наиболее распространенные перекрестные наклоны. что является «крутизной» фильтра (насколько эффективно они блокируют частоты за пределами частоты кроссовера).
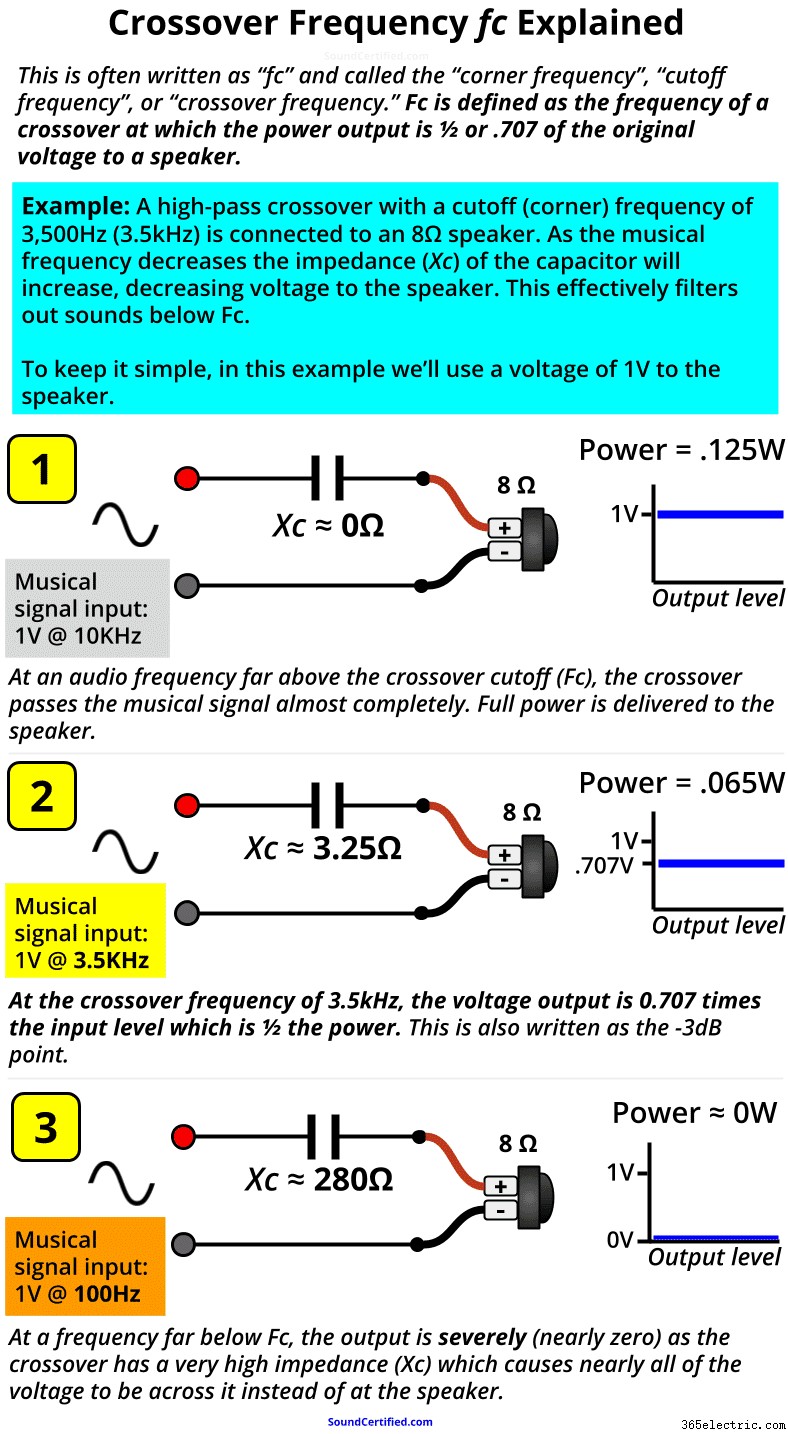
Частота кроссовера, обычно обозначаемая как Fc , представляет собой точку звуковой частоты в герцах (Гц), при которой кроссовер обеспечивает выходную мощность -3 дБ (1/2) на динамик. Fc — это отметка, после которой звуковые частоты будут сильно уменьшены, чтобы они не достигли динамика.
После точки частоты кроссовера (Fc) выходная мощность кроссовера будет падать все больше и больше, при этом все меньше и меньше мощности передается на динамик. Так получилось, что при Fc выходное напряжение на нагрузку (динамик) составляет 0,707 x входное напряжение, что означает, что вы можете рассчитать падение децибел на основе выходного напряжения по сравнению с входным напряжением.
Почему важны частоты кроссовера
При проектировании кроссоверов динамиков частота кроссовера (fc ) используется как своего рода линия, которая отмечает, где мы хотим начать блокировать звуковые частоты, посылаемые на динамик. Обычно он основывается на спецификациях, предоставленных производителем динамиков, в которых перечислены звуковые частоты, которые динамик может воспроизводить с хорошим звуковым откликом и без искажений.
Например, твитеры не могут воспроизводить басовые ноты из музыки и даже могут быть ими повреждены. Зная это, мы хотели бы выбрать достаточно высокую частоту кроссовера, чтобы блокировать басовые ноты, посылаемые на твитеры, чтобы предотвратить искажение или повреждение. (Обычно твитеры имеют частоту кроссовера в тысячах герц [для краткости пишется как килогерц или кГц], например 3,5 кГц, 5 кГц и т. д. хорошо выше диапазона низких и средних частот в музыке).
Частота кроссовера также иногда называется угловой частотой или частота среза поскольку мы думаем с точки зрения того, как звуки «обрезаются» после этой точки.
Частота кроссовера Fc очень важно для перекрестного дизайна
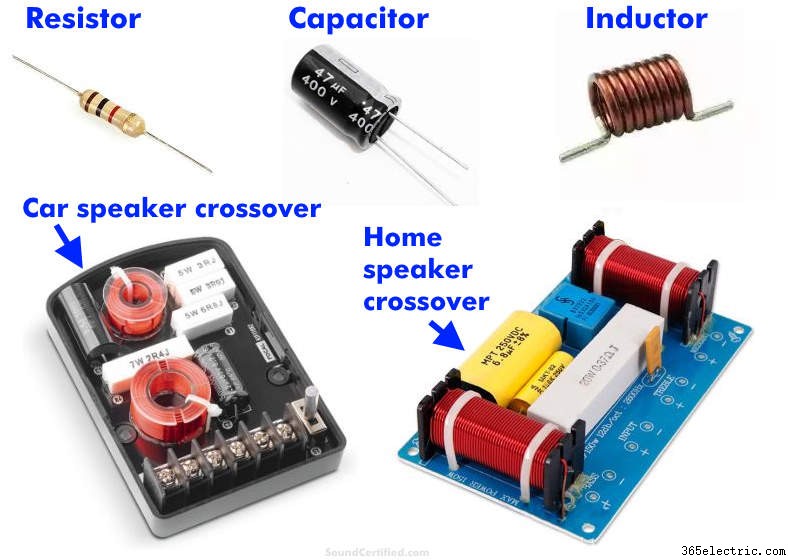
Кроссоверы динамиков (также называемые «пассивными», так как они не используют электроэнергию для работы) используют конденсаторы и катушки индуктивности, которые выбираются на основе доступных деталей и их стоимости. Кроссовер создается на основе начальной частоты Fc и корректируется по мере необходимости в соответствии с целями проекта.
Использование частоты кроссовера Fc в качестве отправной точки позволяет разработчикам акустических систем рассчитать номиналы необходимых компонентов (конденсаторов и катушек индуктивности) в зависимости от импеданса громкоговорителя. Поскольку вы не можете покупать детали любой стоимости, Fc, который мы получаем в зависимости от того, что мы хотим, является хорошей отправной точкой, с которой мы можем работать и корректировать по мере необходимости для работы с деталями в зависимости от доступности, цены и других факторов.
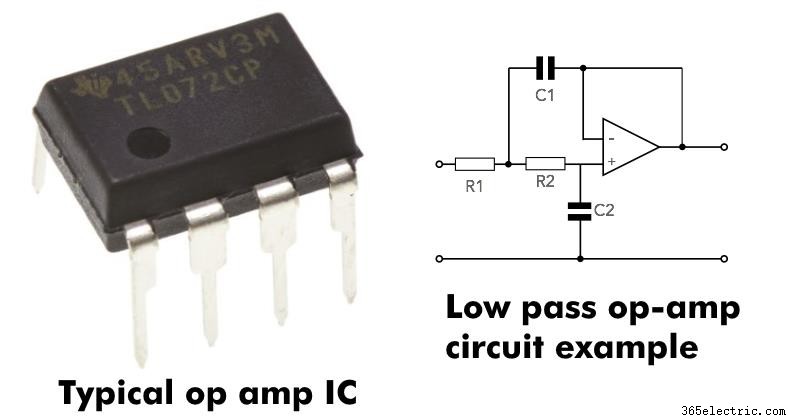
Операционные усилители, также называемые операционными усилителями, являются наиболее важным строительным блоком электронных кроссоверов. Электронные кроссоверы выполняют точно такую же работу (и имеют такое же базовое поведение), что и пассивные (динамики) кроссоверы. Разница в том, что они работают с сигналами низкого уровня до они усиливаются, в то время как пассивные кроссоверы работают с усиленными сигналами после выход усилителя.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: В этой статье я описываю, как работают пассивные (не электронные, без питания) кроссоверы и Fc, но принципы для электронных фильтров точно такие же.Так же, как и их более крупные аналоги на основе пассивных конденсаторов или катушек индуктивности, кроссоверы на основе операционных усилителей имеют такие же наклоны и поведение частоты кроссовера. Они просто делают это с сигналом before он усиливается, а не после него.
Как рассчитать децибелы (дБ) для частоты кроссовера Fc
Все звуковые частоты после частоты кроссовера обрезаются все дальше и дальше со все более крутым снижением — вплоть до того, что они почти полностью блокируются.
In other words, a crossover filters out a range of sounds you’d like to prevent reaching speakers, starting at the crossover frequency.
In the electrical engineering world, we traditionally use decibels (dB) when we talk about power measurements since they’re often non-linear. This just means that mathematically, power is often measured, charted, and tracked using exponential math such as logarithms (“10 to the power of x”, for example).
How crossover frequencies (Fc) and dB are related
Because crossovers reduce power at their output, it’s pretty common to measure the output reduction in decibels. One reason for this is that they have a gentle “slope” (downward curve) rather than a straight line if you were to see them graphed across the full range of audio frequencies.
For that and other reasons, we can measure the power output reduction in dB. To do so, you’ll need to know either (1) the power before and after the speaker/from the amp, or (2) the voltage at the speaker and from the amp.
Knowing those, you can easily calculate the dB output of a crossover with a scientific calculator on your computer or smartphone.
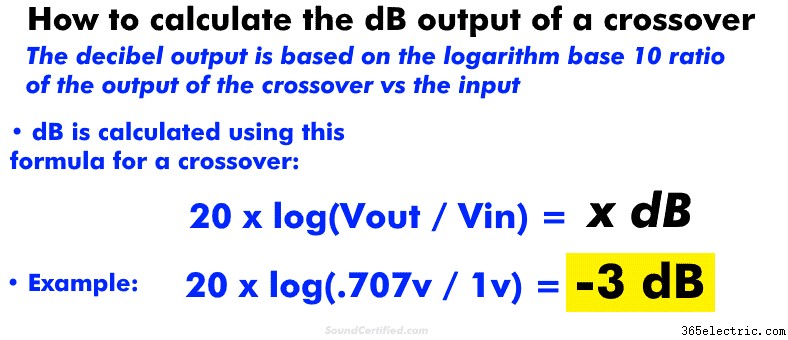
You can calculate dB for a crossover using these formulas:
- For voltage: 20 x log(Vout / Vin ) =x dB
- For power: 10 x log (Power_out / Power_in) =x dB
Understanding crossover signal level in vs out and “negative gain”
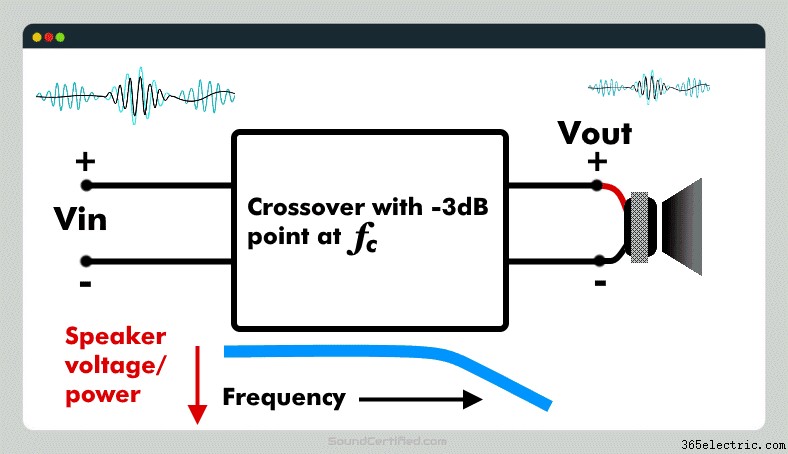
Crossover voltage out (called here “Vout”, the voltage to a speaker delivered from a crossover) can never be higher than the input – that’s not possible. Crossovers can only reduce the input directed to a speaker – they can’t amplify it. Some electronic crossovers do, but those intentionally have a gain on purpose and that’s not common in most cases.
For that reason, you’ll always get a negative dB answer if you do the math for the output of a crossover.
For the record, a negative dB value is used to show a reduction in engineering math while positive usually means a gain or increase in a signal. Amplifiers have a positive dB output (gain) while crossovers and some other components like resistors have a negative gain (a negative dB effect on a signal).
Attenuation is another way of describing a negative gain.
Примечание. the gain control of an amplifier is there to compensate for a high or low input signal level and is a separate section from the crossover circuitry.How a crossover frequency Fc works:example diagram
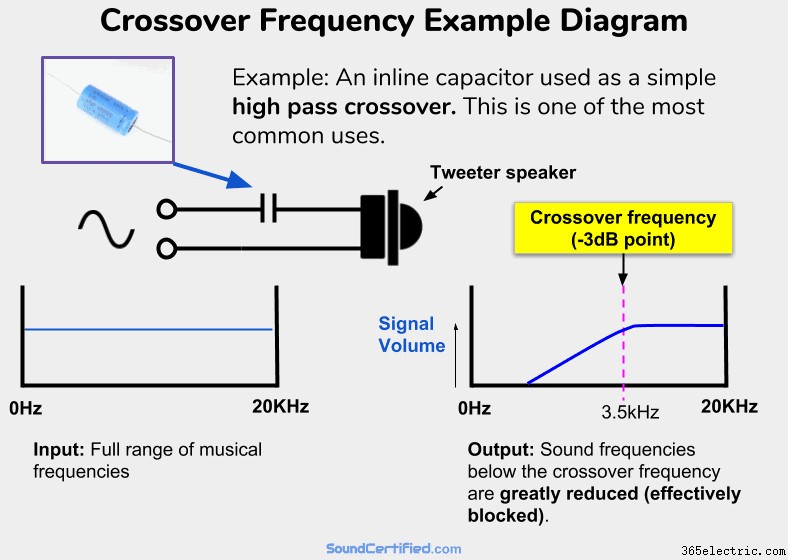
An example of a very common and simple high-pass crossover. A capacitor in series with a speaker will allow higher frequencies (above Fc) to pass with almost no volume or power drop to the speaker. It acts as a zero Ohm resistor (a short circuit wire) in series with it . However, for audio frequencies below Fc, the “resistance” (impedance, called capacitive reactance) of the capacitor will increase, allowing less and less voltage &power to reach the speaker. It will act like a very high-value resistor in series and therefore will block most of the signal from an amp sent to the speaker. In other words, a high-pass filter!
One of the problems I’ve found when we’re talking about this topic is picturing it in your mind. For example, it can be hard to understand what actually happens in real life when actually playing music in the real world vs just some explanation you’ve found on the internet.
All crossovers work the same – understand one, you understand them all (well, mostly!)
One important note I need to make is that the principles are the same regardless of the number of “orders”, or stages, a crossover has. For example, a simple 1st order crossover with a capacitor connected inline with a tweeter works on exactly the same principle as a fancier 2nd order 2-way crossover.
It’s just that the details are a little bit more complicated – not how it works. That part never changes.
There are some crossovers with more sophisticated features &designs I won’t get into here, but for the most part, the majority are all the same and do the same thing to varying degrees. The great thing is that once you understand the basics very well, you’ve got it figured out for the most part!
The fundamentals of how crossovers work with Fc

The most important thing to know is that crossovers work by “absorbing”, or preventing, voltage and power from going to the speakers they’re connected to for the sound frequencies we don’t want them to play.
In the example from my diagram further above, you can see that:
- Above the cutoff frequency Fc, a capacitor acts like an almost zero resistance connection – nothing is blocked and it acts almost like a straight section of wire.
- When audio frequencies begin to reach Fc, the impedance of the crossover goes up, acting like a high-value resistor in series with the speaker. At Fc, the speaker receives only 1/2 the power it would otherwise (which also happens to be .707 times the input voltage from the amp or stereo).
- The farther we go past the Fc limit, the crossover’s impedance is much bigger in Ohms; in fact, past a certain point, it will be several hundred Ohms typically. When that happens the speaker has about 0v and no power to it.
As you can see elsewhere in my article, the “steepness” of the drop in the power &signal level to the speaker depends on the crossover slope. A crossover’s slope is basically just a result of how many “stages”, or crossover sections, are used as needed for the particular speaker system or speakers we’re working with.
Crossovers like you see here and are always in increments of 6 decibels (dB) Per Octave:
- 1st order crossover: a single capacitor or inductor is used, -6dB per octave reduction (not very steep).
- 2nd order crossover: Two components sections are used:one capacitor, one inductor. –12dB/octave reduction (steeper, more effective, very popular).
- 3rd order: two capacitors + 1 inductor or 2 inductors + 1 capacitor are used:–18dB/octave cutoff.
..and so on, with -12db being one of the most common crossover slopes you’ll find for both car audio crossovers and home audio speakers too.
An octave is just a half or double of an audio frequency. For example, 200Hz is an octave of 100Hz, 400Hz is one octave of 200Hz, then 800Hz, and so on. Equalizers and other audio electronics may use other variations with finer numbers like 1/3 octave, for example.Crossover frequency formula math:inductive and capacitive reactance explained
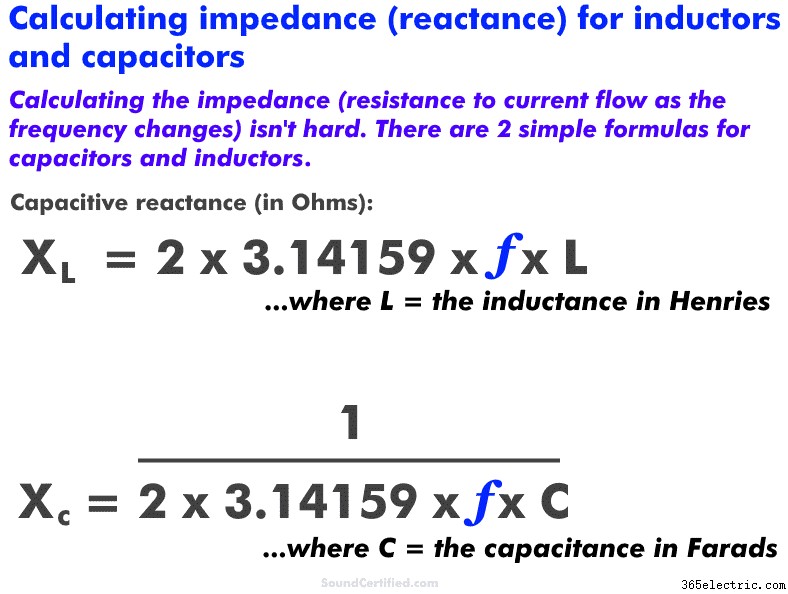
Shown here are the basic formulas for simple 1st order crossovers using capacitors and inductors. Capacitors have an impedance (Ohms) value that depends on the frequency just like inductors do.
Capacitors and inductors have a “resistance” called reactance (in Ohms just like resistance) that depends on the frequency. Here are a few basic things to understand:
- Capacitive reactance increases as the frequency DECREASES. It’s normally written as “Xc.” Capacitance is marked in units of Farads, with most capacitors being values in the microFarad (uF) range, nanoFarad (nF), or even picoFarad (pF).
- Inductive reactance INCREASES as the frequency increases. It’s normally written as “Xl.” Inductance is marked in units of Henries and typically found in units of microHenries (uH) or milliHenries (mH).
Again, it both cases, it’s just a form of impedance much like how a speaker voice coil that has a certain amount of inductance due to the coil of wire inside does. Both are measured in Ohms (Ω).
However, they complement each other and behave pretty much like the opposite of each other. Например:
- Capacitors act like high-pass filters when connected in series and low pass filters in parallel.
- Inductors act like low-pass filters when connected in series and high-pass-filters in parallel.
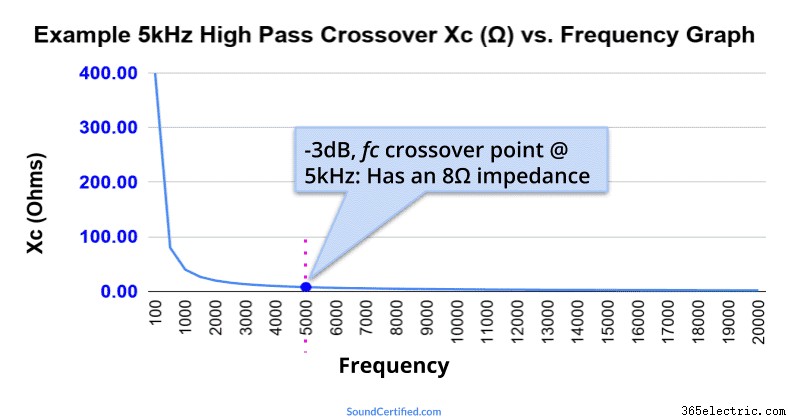
This graph shows an example of a simple high pass capacitor using a 3.98 microFarad capacitor with an 8Ω speaker with a crossover frequency (Fc) of 5kHz. At the Fc value, the impedance is the same as the speaker load (8Ω) which means the speaker power has dropped to 1/2. Further below Fc the impedance grows higher and higher, blocking bass frequencies more and more.
More great crossover and audio articles you’ll love
Don’t miss out on these fantastic articles just waiting for you to read &enjoy!
- Level up your audio knowledge in less than 10 minutes! Learn a ton of details about how crossovers work in this highly detailed article.
- What happens if you use a different speaker impedance with a crossover? It does make a difference, in fact!
- Want better sound from your car or home system? Find out what crossover frequencies to use here.
Need help? Don’t be shy! :)
Got comments, questions, or concerns? Friendly comments and requests for help are always добро пожаловать! Just drop a comment below or reach out via my Contact page here.
Спасибо!
